Introduction:
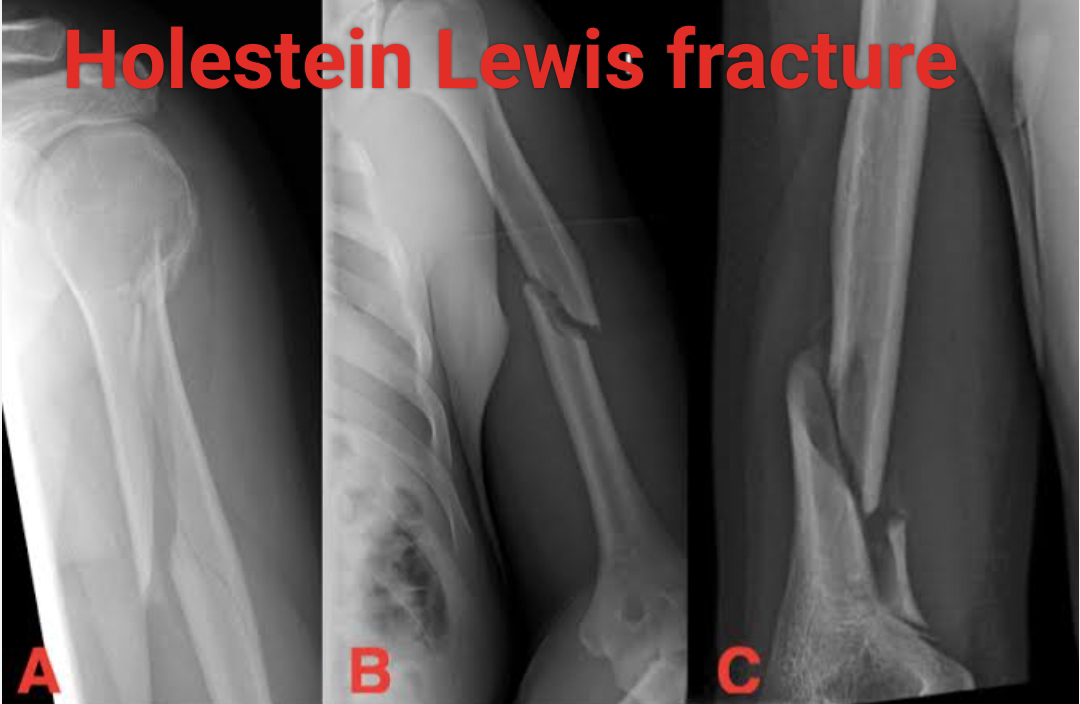
A Holstein-Lewis fracture is a special type of humeral shaft fracture that occurs in the distal end of the humerus. In this fracture the distal end of the humerus is radially displaced, the characteristic feature of a Holstein-Lewis fracture is simple spiral fracture of the distal humerus.
This picture is commonly associated with neuropraxia (temporary nerve dysfunction) of the radial nerve. The incidence of radial nerve palsy in Holstein-Lewis fracture is approximately 22%. In this article you would read everything about physical therapy for holstein-lewis fracture.
Clinical presentation of Holstein-Lewis fracture:
* Pain
* Extremity weakness
* A characteristic deformity known as wrist drop (due to radial nerve dysfunction)
How is an oblique Humerus fracture treated?
An oblique humorous fracture is a type of broken bone where the fracture line runs diagonally across the humerus (upper arm bone) . Let's explore the treatment options for this specific fracture:
1. Non operative treatment:
➡️ Fracture brace: In the initial period of fracture, a fracture brace (which looks like a clamshell) can be used to hold the humorous and proper position.
➡️ Splint: For the reduction of swelling or edema the fracture maybe treated with a splint or sling. As healing progresses, patients can gradually begin using their shoulder and elbow while wearing the brace.
2. Physical therapy:
Regardless of the treatment approach whether it may be operative or non operative, physical therapy is very crucial. It helps the patient to regain the ability to move their arm, and restore strength, with overall improve in function and mobility.
Also read- When should I start physical therapy after a fracture.
How long is Physical therapy for a proximal humerus fracture?
The duration of physical therapy for a proximal humerus fracture can vary depending on the severity of the fracture and the individual’s progress in healing and rehabilitation. Generally, most proximal humerus fractures heal within 3 to 4 months. Here’s a general timeline:
Initial Weeks (1-3 weeks): You may feel the fracture fragments shift as you move your arm, which is normal for fractures not treated with surgery. Gentle exercises to regain motion may begin as soon as you can tolerate it.
Intermediate Phase (3 weeks to 2-3 months): After the initial weeks, more aggressive shoulder strengthening exercises can resume. The goal during this phase is to restore shoulder function.
Long-Term Recovery (3-4 months): Full healing typically takes about three months, but even if surgery is performed, recovery of full function often takes as long as 18 months.
Full Recovery: Can take up to 6 months to a year. Some patients may continue to see improvements for up to 18 months, especially if they had surgery.
It’s important to follow the guidance of physical therapists throughout the recovery process to ensure safe and effective healing.
The most common complication of a midshaft humerus fracture is injury to the radial nerve. This nerve runs in close proximity to the humerus, and a fracture can lead to nerve damage, resulting in symptoms such as weakness, numbness, and difficulty in wrist and finger extension. Another frequent complication is nonunion, where the broken bone ends fail to heal together properly. These complications underscore the importance of careful management and monitoring of humeral shaft fractures.

No comments:
Post a Comment